本記事において使用される図表は,原著論文内の図表を引用しています.
また,本記事の内容は,著者が論文を読み,メモとして短くまとめたものになります.必ずしも内容が正しいとは限らないこと,ご了承ください.
論文情報
タイトル: Multi-Hop Transformer for Document-Level Machine Translation
研究会: NAACL
年度: 2021
キーワード: MT, transformer, Multi-Hop Transformer
URL: https://aclanthology.org/2021.naacl-main.309.pdf
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.naacl-main.309
データセット: TED Talk, OpenSubtitles, Europarl7
概要
Document-level neural machine translationにおいて,Multi-Hopなアーキテクチャを導入することにより,従来手法と比べて精度の高い文脈を考慮した機械翻訳を実現
翻訳者のように,頭の中に翻訳のドラフトを作り,文脈に合わせて適切に修正する流れ(human-like draft-editing)を明示的にモデリング
大きな事前学習済みモデルを使うことなく,使用に足る機械翻訳モデルを実現
提案手法
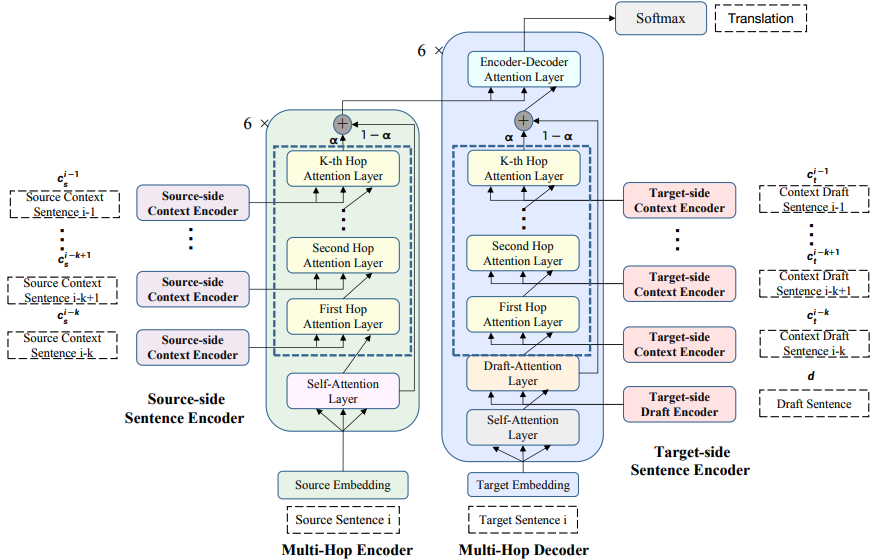
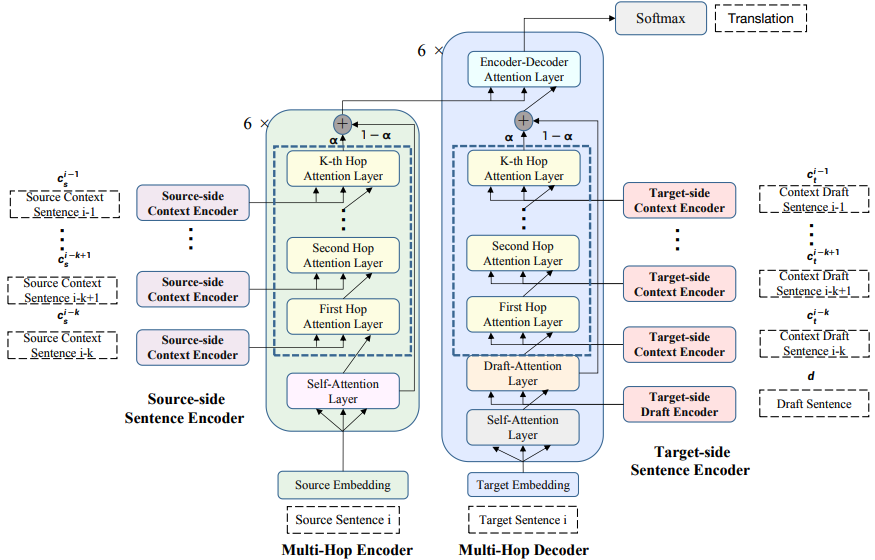
アーキテクチャ周りのこと
Sentence Encoder
source-sideとtarget-sideでそれぞれPretrained Encoderがあり,source contextとtarget draftの分散表現をそれぞれ得る
Multi-Hop Encoder
source-contextにおいて文章ごとのreasoningをして,現在の文章の分散表現を得る
Multi-Hop Decoder
target-side draftから情報を取得して,翻訳の確率分布を得る
そのほかアーキテクチャの工夫
Contet Gating
contextual informationを過剰にutilizeしすぎないように,context gating machanismを採用
contextと現在の文章間の重みを動的にコントロールする
新規性
Docment-level NMTにおける従来手法の問題点
- 文章間のreasoningの特徴づけを明示的に行うことなく,単純にcontextの分散表現を導入
- 推論時にはアクセスできないのに,訓練時には追加入力としてのtarget contextにground-truthなデータを入力 ↑ 訓練時と推論時において状況が異なる
Document-level NMTにおいてMulti-Hop reasoningをモデリングしたMulti-Hop Transformerの提案と提案モデルによるDocument-level NMTの大きな性能改善
target contextにground-truthで訓練すると推論時にはアクセスできないため,他の翻訳モデルの翻訳結果を使用することで,訓練時と推論時の状況を同じにした
実験
Baseline
Transformer
CA-Transformer
CA-HAN
CADec
計算量のオーバーヘッドを改善するためSentence Encoderはそれぞれのsideでパラメータを共有
まとめ
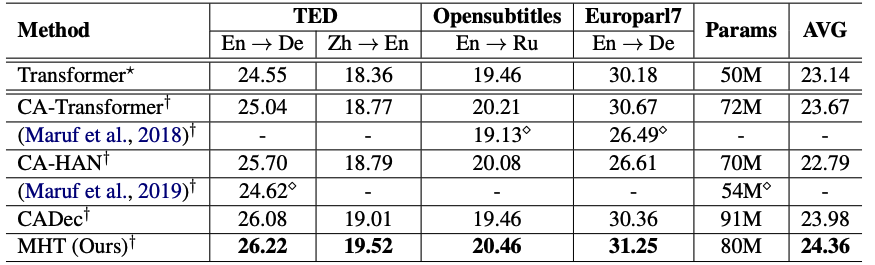
large-scaleな事前学習済み言語モデルを使用することなく,SoTA翻訳クオリティを達成
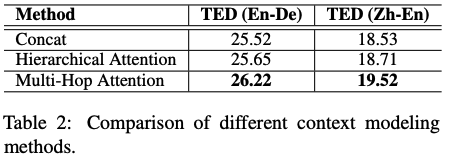
contextを付与するためのAttentionの構造は,ConcatやHierarchicalよりもMulti-HopなAttentionが効果があり
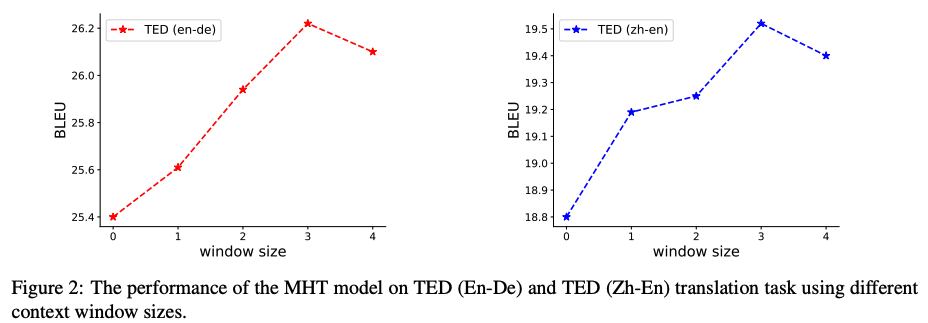
contextを考慮する幅のwindow sizeは大きくするほど効果が上がるわけではなく.3が最も良かった
4以上にすると悪化傾向らしく,本研究ではwindow size = 3 を採用
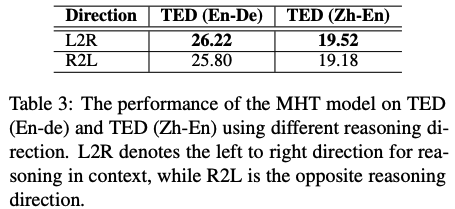
contextにおいてreasoningするときの方向は,一般的な読み順の通りleft-to-rightで順方向にreasoningさせた方が結果は良かった
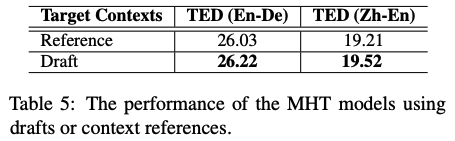
訓練時と推論時にtarget draftに与える文章が異なる問題への対処に関する実験結果
Referenceはground-truthをtarget draftとして与えて訓練,Draftはpre-trained MT systemが生成した翻訳結果をtarget draftとして与えて訓練したモデル
Draftの方が結果がよく,pre-trained MT systemの生成結果をtarget draftとする方法によって訓練時と推論時のギャップの橋渡しになることを示唆する結果
その他(なぜ通ったか?等)
次読みたい論文
Context-Aware Self-Attention Networks
引用
@inproceedings{zhang-etal-2021-multi, title = "Multi-Hop Transformer for Document-Level Machine Translation", author = "Zhang, Long and Zhang, Tong and Zhang, Haibo and Yang, Baosong and Ye, Wei and Zhang, Shikun", booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies", month = jun, year = "2021", address = "Online", publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics", url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.naacl-main.309", doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.naacl-main.309", pages = "3953--3963", abstract = "Document-level neural machine translation (NMT) has proven to be of profound value for its effectiveness on capturing contextual information. Nevertheless, existing approaches 1) simply introduce the representations of context sentences without explicitly characterizing the inter-sentence reasoning process; and 2) feed ground-truth target contexts as extra inputs at the training time, thus facing the problem of exposure bias. We approach these problems with an inspiration from human behavior {--} human translators ordinarily emerge a translation draft in their mind and progressively revise it according to the reasoning in discourse. To this end, we propose a novel Multi-Hop Transformer (MHT) which offers NMT abilities to explicitly model the human-like draft-editing and reasoning process. Specifically, our model serves the sentence-level translation as a draft and properly refines its representations by attending to multiple antecedent sentences iteratively. Experiments on four widely used document translation tasks demonstrate that our method can significantly improve document-level translation performance and can tackle discourse phenomena, such as coreference error and the problem of polysemy.", }