本記事において使用される図表は,原著論文内の図表を引用しています.
また,本記事の内容は,著者が論文を読み,メモとして短くまとめたものになります.必ずしも内容が正しいとは限らないこと,ご了承ください.
論文情報
タイトル: CTRLStruct: Dialogue Structure Learning for Open-Domain Response Generation
研究会: WWW
年度: 2023
キーワード: Dialogue Structure Learning, dialogue system, Contrastive Learning, NLG
URL: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.01094.pdf
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3543507.3583285
コード: https://github.com/lemonsis/CTRLStruct
データセット: PERSONA-CHAT, DailyDialog
概要
対話構造の発見は対話生成において重要
よく構造化されたトピックのフローは背景情報を利用でき,未来のトピックを予測でき,コントローラブルで説明可能な応答生成に役立つ
ラベルなしの情報を用いて,トピックレベルの対話クラスターとその遷移を効果的に見つける対話構造学習のフレームワークCTRLStructを提案
PersonachatとDailyDialogの二つのデータセットを用いて,提案モデルはより一貫した応答を生成し,対話の発話のrepresentationにおいて,いくつかの一般的なsentence embedding手法の性能を超えることを示した.
提案手法
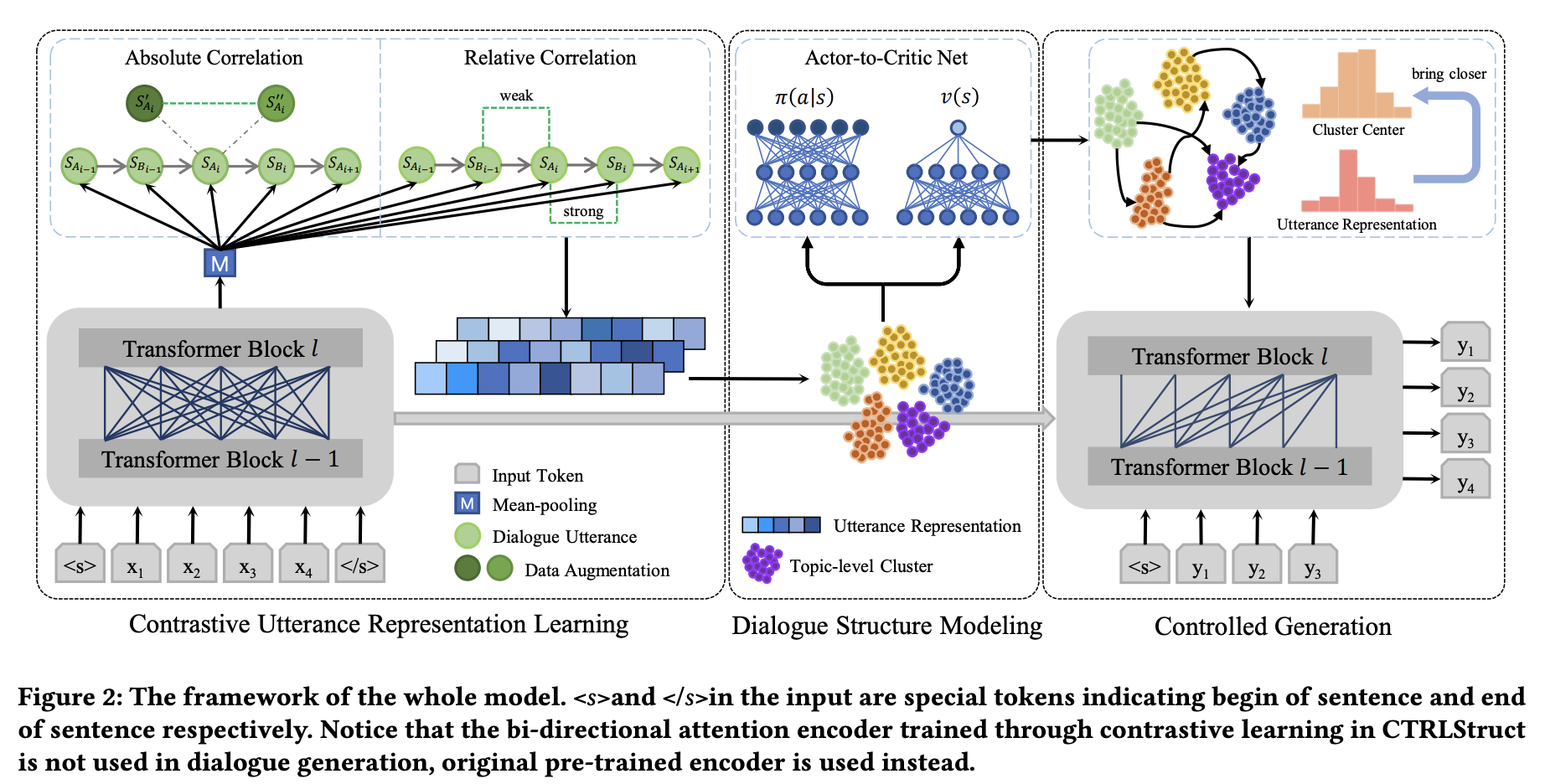
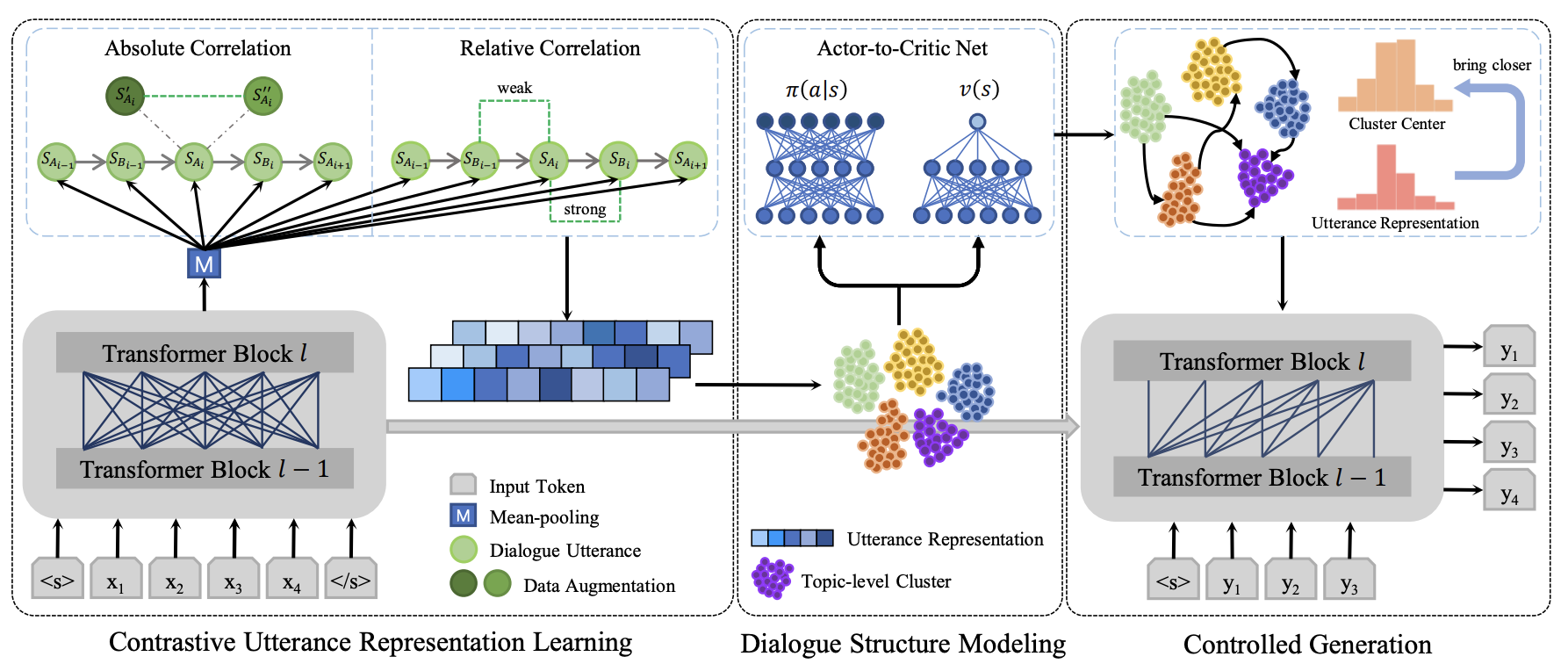
Contrastive Utterance Representation Learning
Absolute Correlation
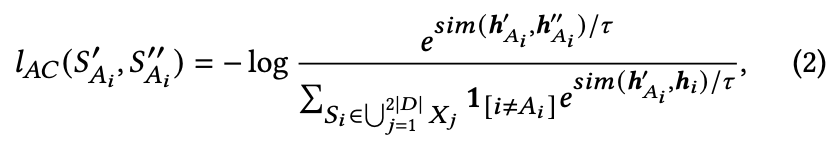
SimCLRに従った自己教師なし対照学習を行う
対象サンプルをデータ拡張して,同サンプルから拡張されたサンプルを近づけるように学習
この時以下の拡張がランダムで行われる(実装より)
- 単語の追加(ContextualWordEmbsAug: insert)
- 単語の置換(ContextualWordEmbsAug: substitute)
- 同義語による置換(SynonymAug)
- 元サンプルのまま
Relative Correlation
ある時点の発話は前の発話と意味的に近く,次の発話とは近い関係性を持つが,その関係性は弱いという想定で実装される
それぞれは,Strong Relativity,Weak Relativityで,対照学習として計算される.
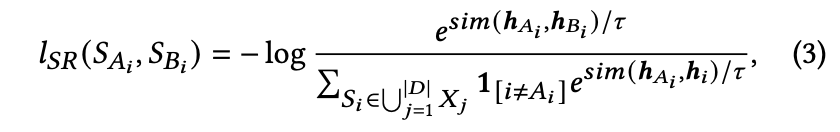
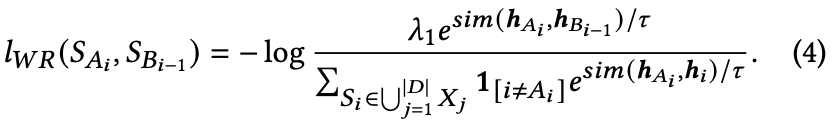
これらは
バッチサイズNに対しては以下のように計算され,最終的な対照学習を用いたエンコーダが構成される.
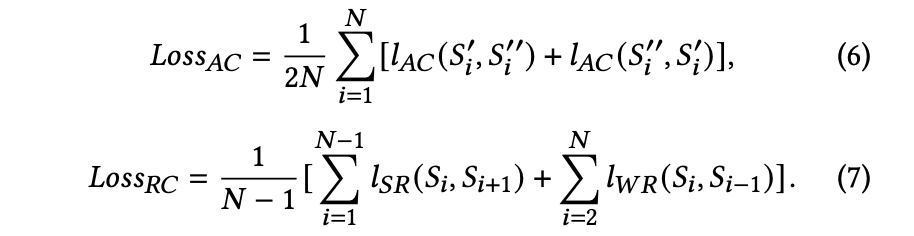
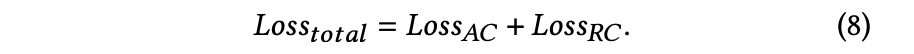
Dialogue Structure Modeling
対話トピックの遷移確率の計算のため,imitation learningを適応する
トピックレベルはエンコーダの埋め込みのクラスタで表現できるが,このクラスタが強化学習における状態となる
元の状態はutterance representationで連続値だが,遷移先の状態をクラスタidとすると離散値になるため,クラスタ中心のベクトルを状態遷移先とすることで,状態を連続値として表現する
タスク設定としては,
この設定を踏まえ,MLEによって,ポリシー
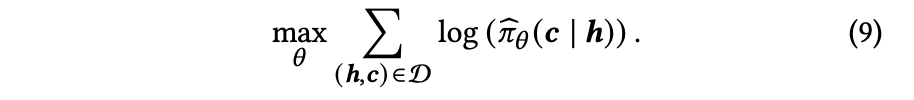
連続値の行動と状態におけるポリシーを表現するために正規分布を適応し,状態
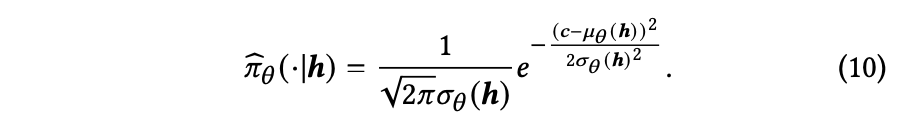
(9)と(10)から,以下の式に変形される
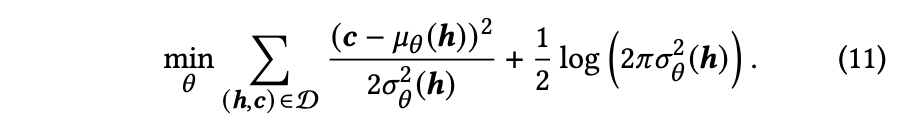
A2CNet (Actor-to-Critice network)を用いて,
報酬は得られないので,これは考慮していない
分散
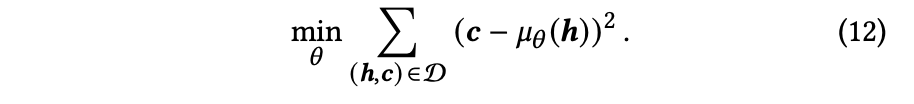
これをニューラルネットで解き,ポリシーを予測する
Controlled Generation
NLLロスとKLダイバージェンスロスによってデコーダを最適化する
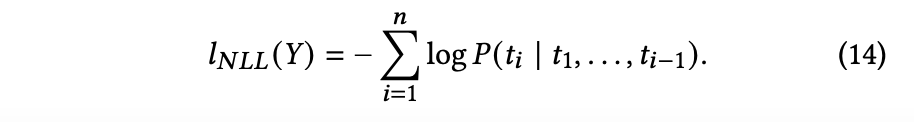
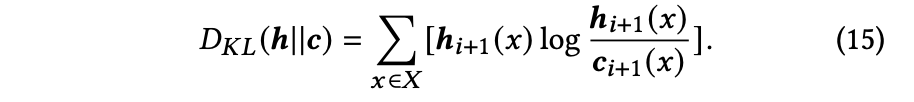
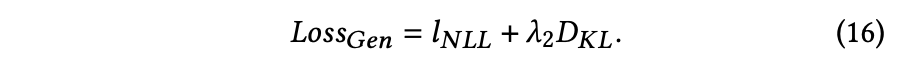
新規性
- ラベルなしのコーパスを用いて,対話構造を見つけ,応答生成をコントロールするフレームワークを提案
- 対話構造の学習は,これまではタスク指向対話で主に取り組まれていたため,オープンドメイン対話に取り組んだことも新しい
- 対照学習を行うエンコーダによって,トピックレベルの対話構造モデリングの性能を改善するためにutterance representationの学習を増強する
- imitation learning手法を提案し,トピックレベルの対話遷移確率の推定を行い,高品質な対話構造学習を行う.
実験
次の疑問を実験により明らかにする
- 他の強い対話生成モデルに対して,どのようにしてCTRLStructはオープンドメイン対話において動作するか?
- 本当に提案モデルは応答のトピックをコントロールするか?発見された対話構造は応答生成に役立つか?
- 他のsentence embedding手法に対して,提案モデルはutterance representationにおいてどのように動作するか?
- 提案モデルの汎化性能は?他のタイプのバックボーンを用いたモデルにも適応可能?
データセットには,PersonaChatとDailyDialog
比較モデル
- Seq2Seq
- CVAE
- BART (large)
- DialoGPT (medium)
- BlenderBot (2.7B)
まとめ
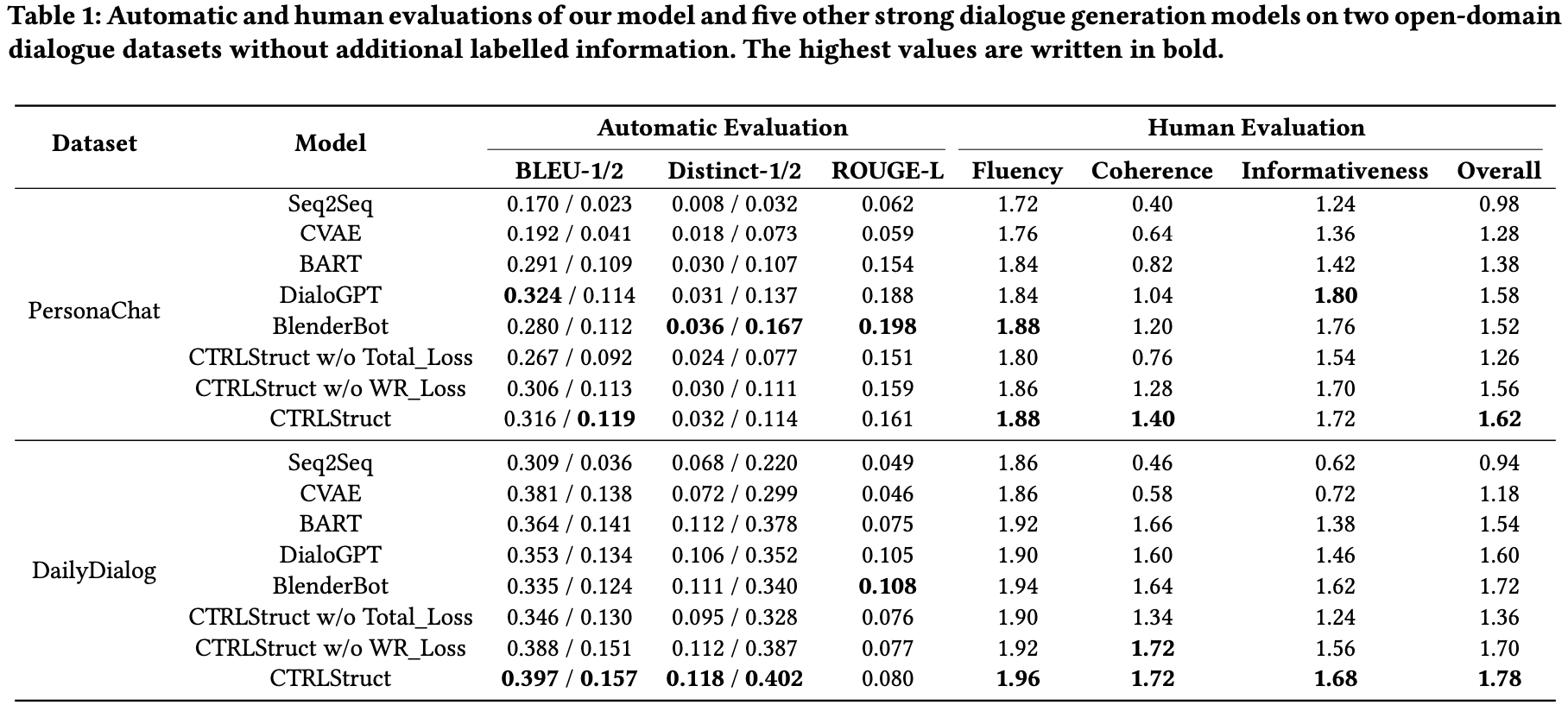
CTRLStructは全体的に他のモデルの性能を超える
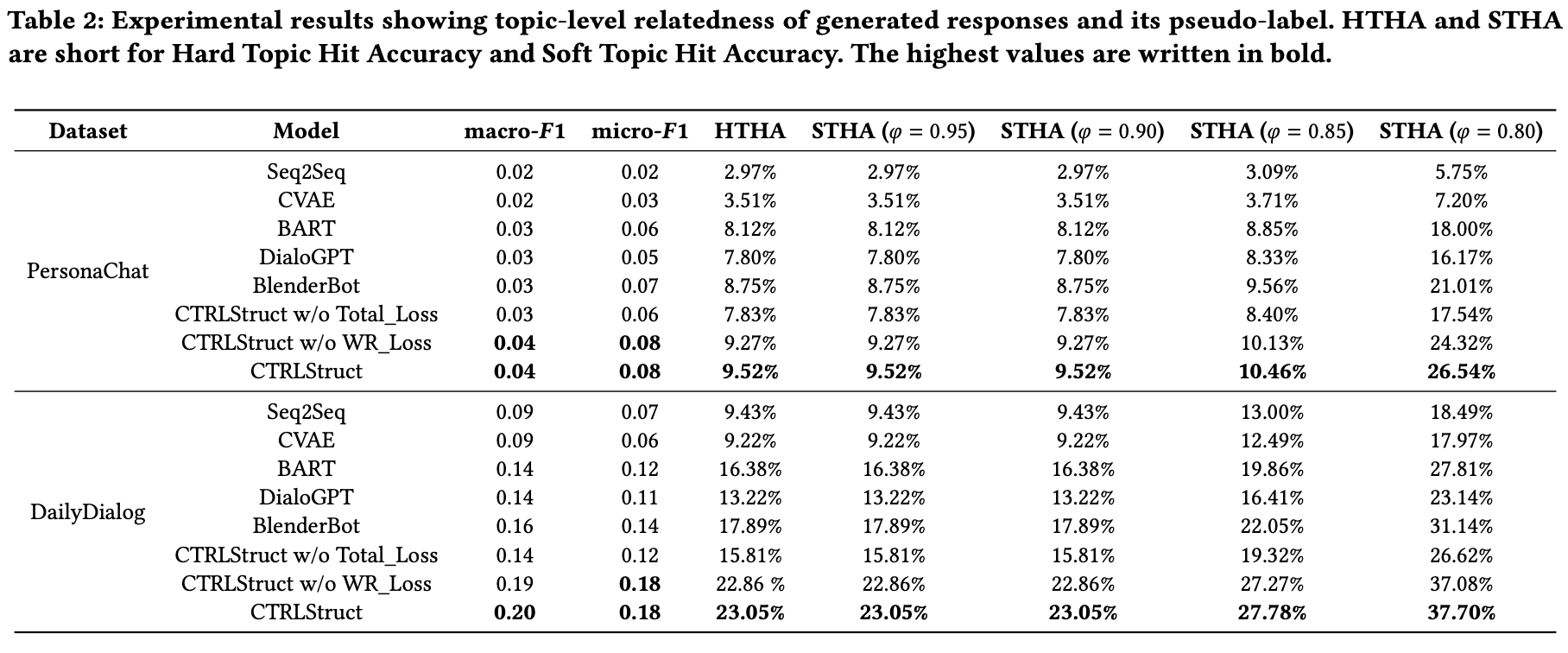
HTHA (Hard Topic Hit Accuracy),STHA (Soft Topic Hit Accuracy)
与えられたkカテゴリと生成されたサンプルのマルチラベル分類で定式化され,トピック分類の性能を評価
(真のラベルは存在しないため,CTRLStructのクラスタリングのプロセスで得られるラベルを擬似ラベルとして使用.)
PersonaChatはDailyDialogと違い,トピックの多様性が低い
→ 実際に持っているトピックよりも多いトピックカテゴリを設定してしまったため(トピックのクラスタ数?),多くのノイズが現れて,CTRLStructが動作しなかったと考えられる
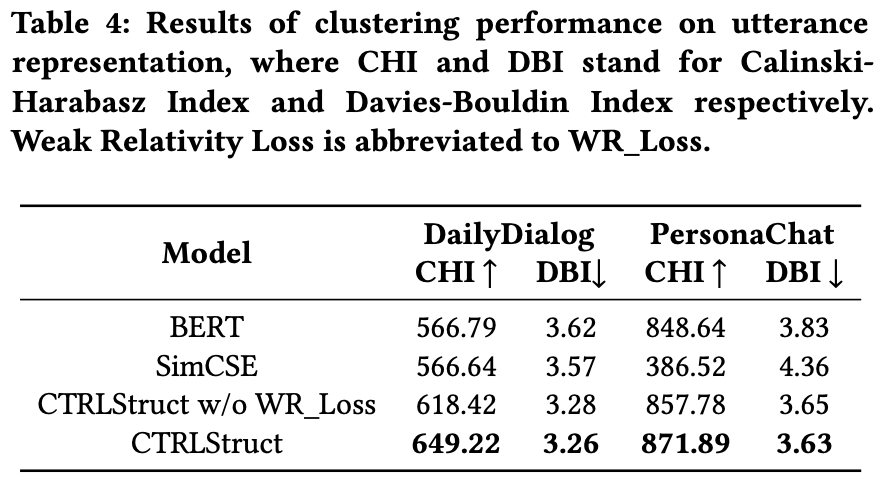
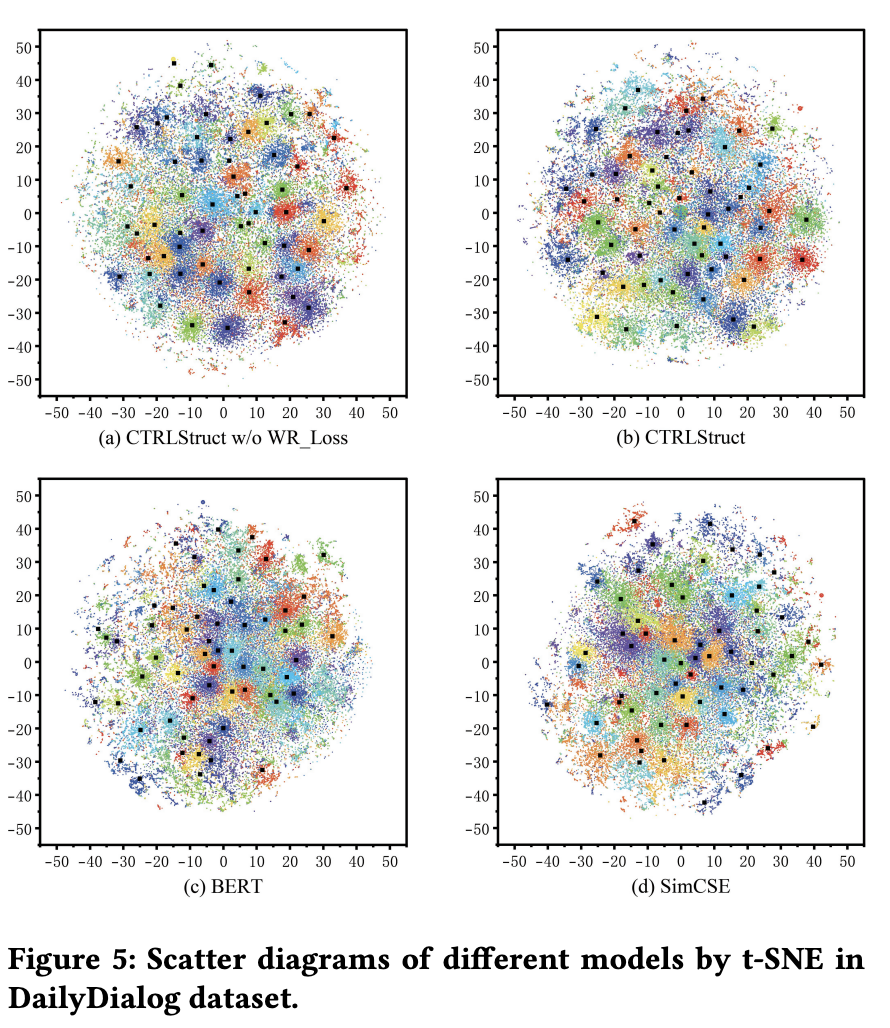
utterance representationの評価
PersonaChatでは,SimCSEがBERTよりも低い性能
CTRLStructはどの指標,どのデータセットでも比較手法を超える性能
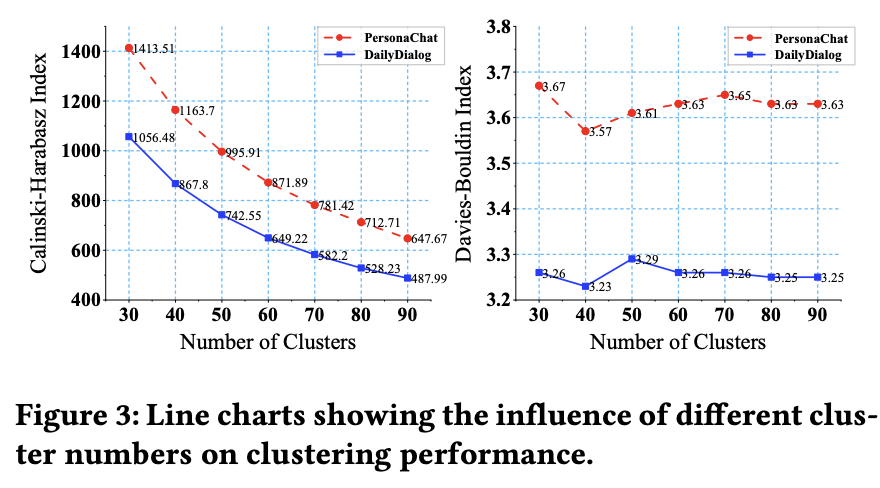
Figure3から,CTRLStructは,クラスタ数に対してロバストと言えるらしい
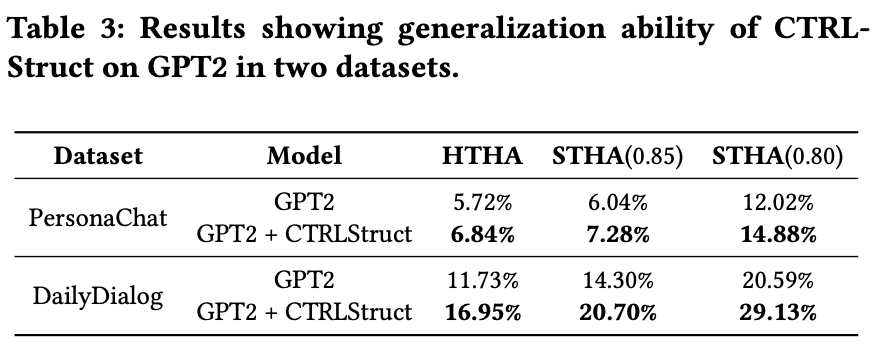
GPT2を用いて,他のバックボーンに対するCTRLStructの効果を検証
GPT2に対して適応させても性能が向上していることがわかった.
ただし,この手法はTransformerを想定しているため,Transformer構造を持たないモデルに対しては適応できない可能性がある
その他(なぜ通ったか?等)
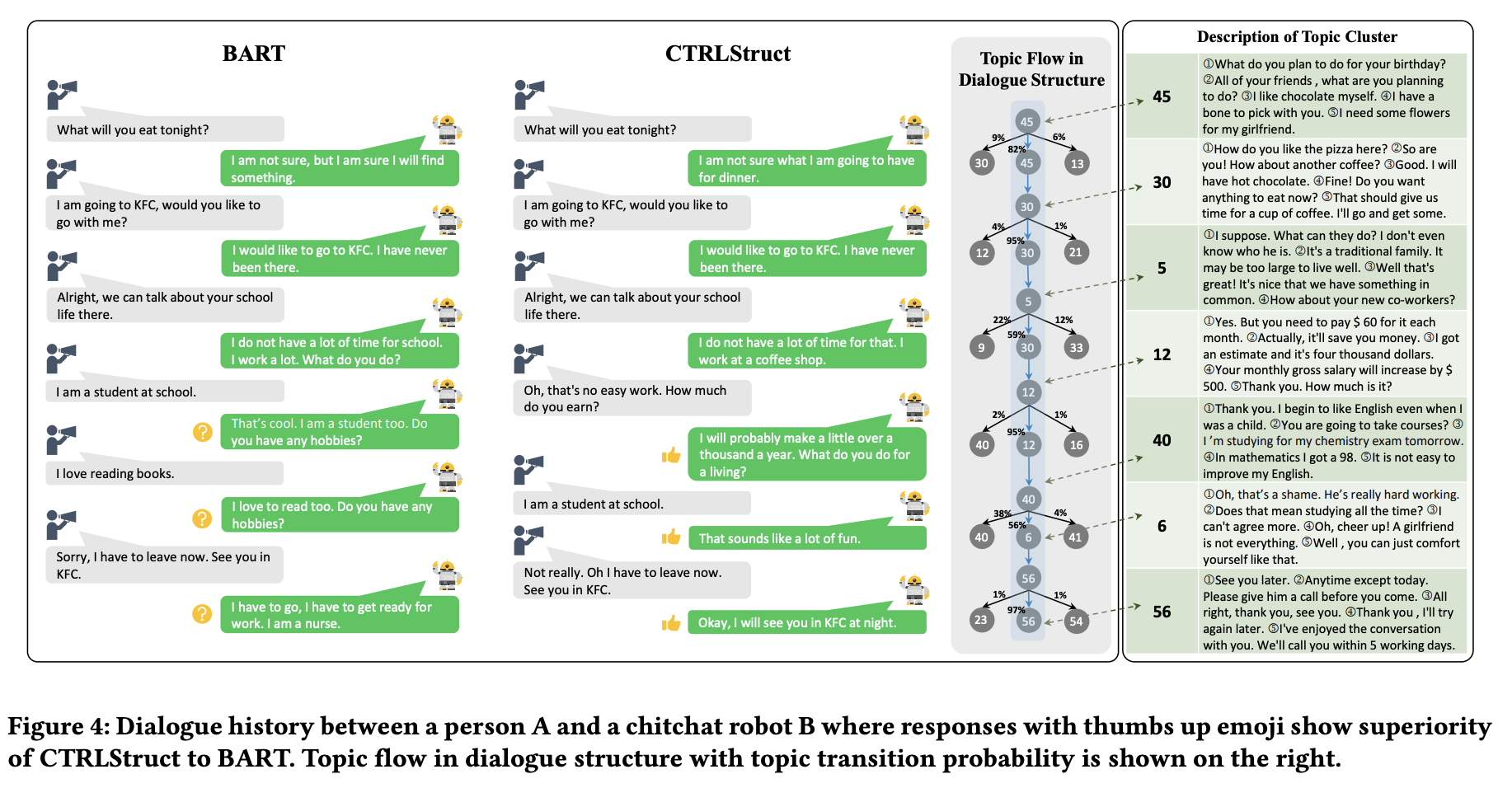
次読みたい論文
引用
@inproceedings{10.1145/3543507.3583285, author = {Yin, Congchi and Li, Piji and Ren, Zhaochun}, title = {CTRLStruct: Dialogue Structure Learning for Open-Domain Response Generation}, year = {2023}, isbn = {9781450394161}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3543507.3583285}, doi = {10.1145/3543507.3583285}, abstract = {Dialogue structure discovery is essential in dialogue generation. Well-structured topic flow can leverage background information and predict future topics to help generate controllable and explainable responses. However, most previous work focused on dialogue structure learning in task-oriented dialogue other than open-domain dialogue which is more complicated and challenging. In this paper, we present a new framework CTRLStruct for dialogue structure learning to effectively explore topic-level dialogue clusters as well as their transitions with unlabelled information. Precisely, dialogue utterances encoded by bi-directional Transformer are further trained through a special designed contrastive learning task to improve representation. Then we perform clustering to utterance-level representations and form topic-level clusters that can be considered as vertices in dialogue structure graph. The edges in the graph indicating transition probability between vertices are calculated by mimicking expert behavior in datasets. Finally, dialogue structure graph is integrated into dialogue model to perform controlled response generation. Experiments on two popular open-domain dialogue datasets show our model can generate more coherent responses compared to some excellent dialogue models, as well as outperform some typical sentence embedding methods in dialogue utterance representation. Code is available in GitHub1.}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023}, pages = {1539–1550}, numpages = {12}, keywords = {Dialogue Structure Learning, Imitation Learning, Utterance Representation, Open-Domain Dialogue Generation, Contrastive Learning}, location = {Austin, TX, USA}, series = {WWW '23} }